Brain is the central organ of the human body. It is extremely complex and sophisticated. The functions of the brain were found by the ancient Egyptians and Greeks in 400 BC. It was Hippocrates who first discovered that brain played an important role in sensation and intelligence. Nowadays, everyone understand the importance of having the brain, but most of us don’t know much about it, so here are some interesting facts for you.
1) There are no pain receptors in the brain, so the brain can feel no pain.
2) The human brain is the fattest organ in the body and may consists of at least 60% fat.
3) Neurons develop at the rate of 250,000 neurons per minute during early pregnancy.
4) Humans continue to make new neurons throughout life in response to mental activity.
5) Alcohol interferes with brain processes by weakening connections between neurons.
6) Altitude makes the brain see strange visions – Many religions

involve special visions that occurred at great heights. For example, Moses encountered a voice emanating from a burning bush on Mount Sinai and Muhammad was visited by an angel on Mount Hira. Similar phenomena are reported by mountain climbers, but they don’t think it’s very mystical. Many of the effects are attributable to the reduced supply of oxygen to the brain. At 8,000ft or higher, some mountaineers report perceiving unseen companions, seeing light emanating from themselves or others, seeing a second body like their own, and suddenly feeling emotions such as fear. Oxygen deprivation is likely to interfere with brain regions active in visual and face processing, and in emotional events.
7) Reading aloud and talking often to a young child promotes brain development.
8 ) Information travels at different speeds within different types of

neurons. Not all neurons are the same. There are a few different types within the body and transmission along these different kinds can be as slow as 0.5 meters/sec or as fast as 120 meters/sec
.9) The capacity for such emotions as joy, happiness, fear, and shyness are already developed at birth. The specific type of nurturing a child receives shapes how these emotions are developed.
10) The left side of your brain (left hemisphere) controls the right side of your body; and, the right side of your brain (right hemisphere) controls the left side of your body.
11) Children who learn two languages before the age of five alters the brain structure and adults have a much denser gray matter.
12) Information can be processed as slowly as 0.5 meters/sec or as fast as 120 meters/sec (about 268 miles/hr).
13) While awake, your brain generates between 10 and 23 watts of power–or enough energy to power a light bulb.
14) The old adage of humans only using 10% of their brain is not true. Every part of the brain has a known function.
15) A study of one million students in New York showed that

students who ate lunches that did not include artificial flavors, preservatives, and dyes did 14% better on IQ tests than students who ate lunches with these additives.
16) For years, scientists believed that tinnitus was due to a function within the mechanics of the ear, but newer evidence shows that it is actually a function of the brain.
17) Every time you recall a memory or have a new thought, you are creating a new connection in your brain.
18) Memories triggered by scent have a stronger emotional connection, therefore appear more intense than other memory triggers.
19) Each time we blink, our brain kicks in and keeps things illuminated so the whole world doesn’t go dark each time we blink (about 20,000 times a day).
20) Laughing at a joke is no simple task as it requires activity in five different areas of the brain.
21) The average number of thoughts that humans are believed to experience each day is 70,000.
22) There are two different schools of thought as to why we dream: the physiological school, and the psychological school. While many theories have been proposed, not single consensus has emerged as to why we dream. Some researchers suggest that dreams serve no real purpose, while other believe that dreaming is essential to mental, emotional and physical well-being. One theory for dreaming suggests dreams serve to clean up clutter from the mind.
23) The Hypothalamus part of the brain regulates body temperature much like a thermostat. The hypothalamus knows what temperature your body should be (about 98.6 Fahrenheit or 37 Celsius), and if your body is too hot, the hypothalamus tells it to sweat. If you’re too cold, the hypothalamus makes you start shivering. Shivering and sweating helps get your body’s temperature back to normal.
24) Approximately 85,000 neocortical neurons are lost each day in your brain. Fortunately, his goes unnoticed due to the built-in redundancies and the fact that even after three years this loss adds up to less than 1% of the total.
25) Differences in brain weight and size do not equal differences in mental ability. The weight of Albert Einstein’s brain was 1,230 grams that is less than an average weight of the human brain.
26) A living brain is so soft you could cut it with a table knife.
27) There are about 100,000 miles of blood vessels in the brain.
28)

London taxi drivers ,famous for knowing all the London streets by heart, have a larger than normal hippocampus, especially the drivers who have been on the job longest. The study suggests that as people memorize more and more information, this part of their brain continues to grow.
29) The brain can live for 4 to 6 minutes without oxygen, and then it begins to die. No oxygen for 5 to 10 minutes will result in permanent brain damage.
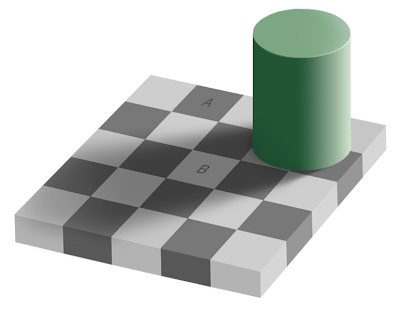
30) Our brain often fools us. It often perceives things differently from the reality. Look at those pictures. Square A and B are actually the same
shade of gray.
 Leave your comments..
Leave your comments..

 involve special visions that occurred at great heights. For example, Moses encountered a voice emanating from a burning bush on Mount Sinai and Muhammad was visited by an angel on Mount Hira. Similar phenomena are reported by mountain climbers, but they don’t think it’s very mystical. Many of the effects are attributable to the reduced supply of oxygen to the brain. At 8,000ft or higher, some mountaineers report perceiving unseen companions, seeing light emanating from themselves or others, seeing a second body like their own, and suddenly feeling emotions such as fear. Oxygen deprivation is likely to interfere with brain regions active in visual and face processing, and in emotional events.
involve special visions that occurred at great heights. For example, Moses encountered a voice emanating from a burning bush on Mount Sinai and Muhammad was visited by an angel on Mount Hira. Similar phenomena are reported by mountain climbers, but they don’t think it’s very mystical. Many of the effects are attributable to the reduced supply of oxygen to the brain. At 8,000ft or higher, some mountaineers report perceiving unseen companions, seeing light emanating from themselves or others, seeing a second body like their own, and suddenly feeling emotions such as fear. Oxygen deprivation is likely to interfere with brain regions active in visual and face processing, and in emotional events. neurons. Not all neurons are the same. There are a few different types within the body and transmission along these different kinds can be as slow as 0.5 meters/sec or as fast as 120 meters/sec.
neurons. Not all neurons are the same. There are a few different types within the body and transmission along these different kinds can be as slow as 0.5 meters/sec or as fast as 120 meters/sec. students who ate lunches that did not include artificial flavors, preservatives, and dyes did 14% better on IQ tests than students who ate lunches with these additives.
students who ate lunches that did not include artificial flavors, preservatives, and dyes did 14% better on IQ tests than students who ate lunches with these additives. London taxi drivers ,famous for knowing all the London streets by heart, have a larger than normal hippocampus, especially the drivers who have been on the job longest. The study suggests that as people memorize more and more information, this part of their brain continues to grow.
London taxi drivers ,famous for knowing all the London streets by heart, have a larger than normal hippocampus, especially the drivers who have been on the job longest. The study suggests that as people memorize more and more information, this part of their brain continues to grow.











 Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer project scientist Peter Eisenhardt stands next to the fully assembled satellite.
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer project scientist Peter Eisenhardt stands next to the fully assembled satellite.